A HEAD-TO-HEAD COMPARISON OF IXEKIZUMAB AND ADALIMUMAB IN BIOLOGIC-NAÏVE PATIENTS WITH ACTIVE PSORIATIC ARTHRITIS: 52-WEEK EFFICACY AND SAFETY OUTCOMES FROM A RANDOMIZED, OPEN-LABEL, BLINDED ASSESSOR STUDY


Background/Purpose:
Multiple biologic DMARDs (bDMARDs) are available for treatment of PsA, but there are few direct comparisons of their efficacy and safety. Furthermore, efficacy of biologics with or without concomitant MTX is one of the most clinically relevant questions for clinicians. Ixekizumab (IXE) was superior to adalimumab (ADA) at Week (Wk) 24 for simultaneous achievement of ACR50 and 100% improvement from baseline in the Psoriasis Area and Severity Index (PASI100) (primary endpoint) in patients (pts) with active PsA (SPIRIT-H2H) (Mease et al, Ann Rheum Dis 2019). We report final Wk 52 efficacy and safety, and efficacy in subgroups defined by concomitant MTX use at Wk 52 of SPIRIT-H2H.
Methods:
Pts with active PsA fulfilling Classification for Psoriatic Arthritis (CASPAR) criteria, ≥3/66 tender and ≥3/68 swollen joints, ≥3% psoriasis body surface area (BSA) involvement, no prior treatment with bDMARDs, and prior inadequate response to ≥1 conventional synthetic DMARD (csDMARD), were randomized 1:1 to open-label IXE or ADA (label dosing according to presence/absence of moderate-to-severe psoriasis [baseline BSA≥10%, PASI≥12, and static Physician’s Global Assessment≥3]) through 52 wks. Outcomes included the percentage of pts achieving both ACR50 + PASI100 simultaneously, ACR20/50/70, PASI75/90/100, Nail Psoriasis Severity Index (NAPSI)=0, Minimal Disease Activity (MDA), Very Low Disease Activity (VLDA, defined as MDA 7/7), Disease Activity in Psoriatic Arthritis Low Disease Activity (DAPSA LDA), DAPSA remission, Leeds Enthesitis Index (LEI)=0, Spondyloarthritis Research Consortium of Canada (SPARCC) Enthesitis Index=0, Leeds Dactylitis Index-Basic (LDI-B)=0, and HAQ-Disability Index (HAQ-DI) ≥0.35 change from baseline. Efficacy was also analyzed in subgroups based on concomitant MTX. Efficacy outcomes were analyzed using logistic regression with nonresponder imputation for missing data. There were no adjustments for multiple comparisons. Safety outcomes are summarized for pts who received ≥1 dose of study treatment.
Results:
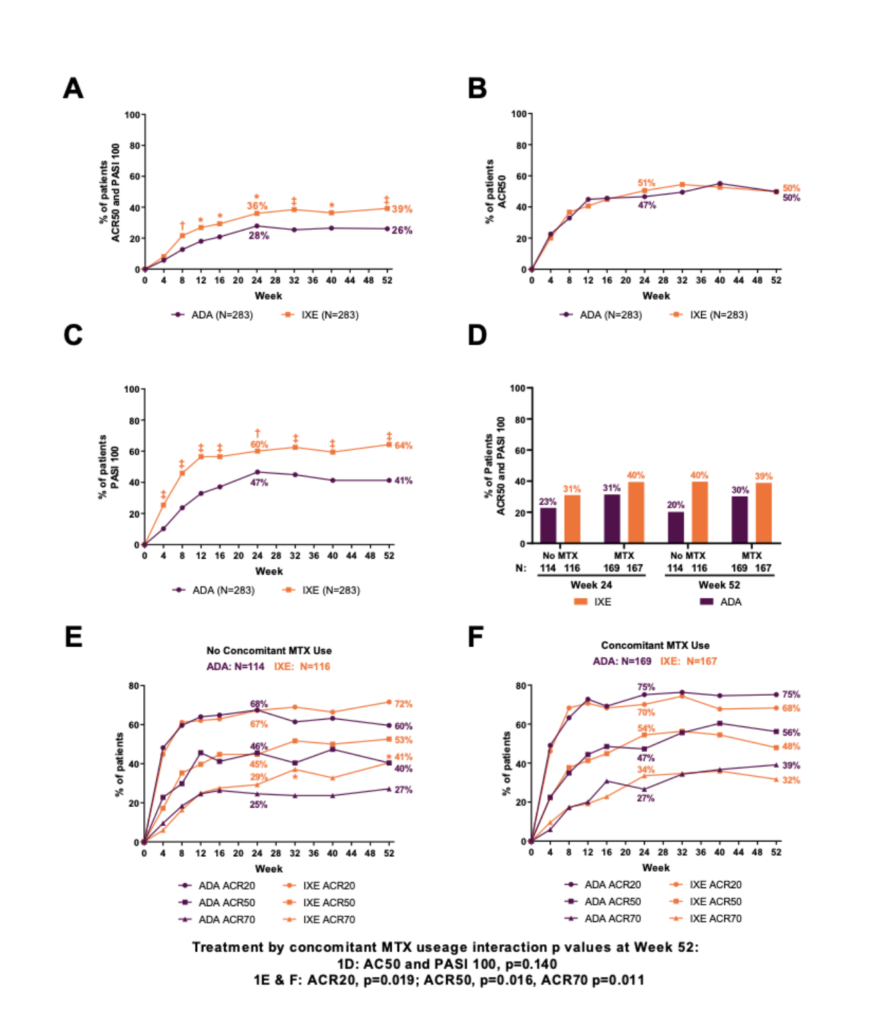
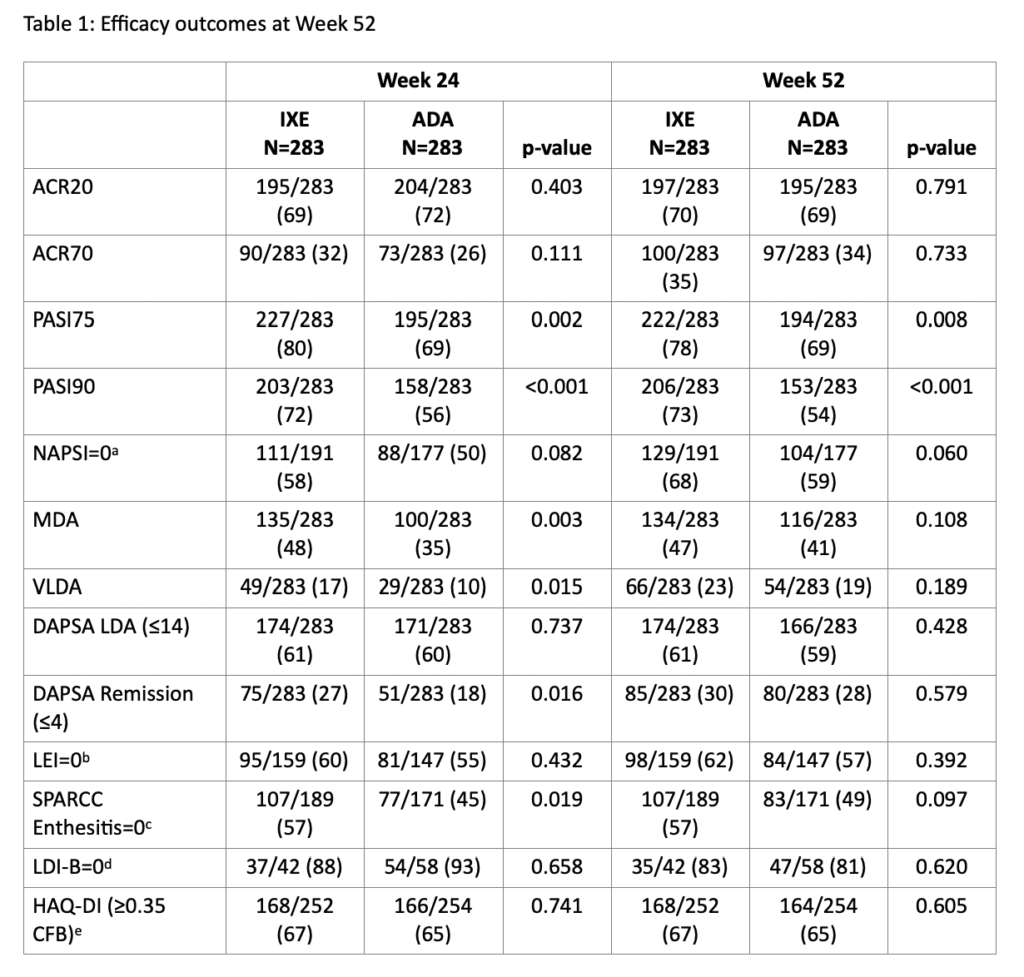
Overall, 87% (246/283) and 84% (237/283) of pts randomized to IXE and ADA, respectively, completed Wk 52. IXE provided significantly greater response than ADA for simultaneous ACR50 + PASI100 through Wk 52 (Figure 1A). IXE performed at least as well as ADA at Wk 52 for all other outcomes (Figure 1B, 1C, Table 1). Simultaneous ACR50 + PASI100 response with IXE was numerically greater than ADA, regardless of concomitant MTX use (Figure 1D). MTX use by treatment interaction was significant for ACR20/50/70 at Wk 52 (Figure 1E-F). Treatment-emergent adverse events (AEs) occurred in 73.9% (IXE) and 68.6% (ADA) of pts. Serious AEs occurred in 4.2% (IXE) and 12.4% (ADA) of pts, and discontinuations due to AEs occurred in 4.2% (IXE) and 7.4% (ADA) of patients; no deaths occurred. (Table 2).
Conclusion:
IXE provided significantly greater simultaneous joint and skin improvement versus ADA as early as Wk 8 and through Wk 52. IXE performed at least as well as ADA across multiple PsA domains including musculoskeletal and skin domains through Wk 52. Safety outcomes for IXE and ADA were consistent with their previously established safety profiles.
Figures/Tables:
Figure 1: Percentage of patients achieving (A) simultaneous ACR50 and PASI100 response, (B) ACR50 response, and (C) PASI 100 through Week 52. (D) Percentage of patients achieving simultaneous ACR50 and PASI100 response at Week 24 and 52 by concomitant MTX use during the study. Percentage of patients achieving ACR20/50/70 response with (E) no concomitant MTX use or (F) concomitant MTX use through Week 52 of the study. Of 392 patients with concomitant csDMARDs use, 336 patients were on MTX and 56 were on other csDMARDs (leflunomide, sulfasalazine, or cyclosporine). *p<0.05, †p<0.01, ‡p<0.001.


Values are presented as n/N (%)
After the initial database lock and analysis run, nine patients who met baseline criteria for active psoriasis had baseline PASI=0 and BSA≥3% (a medical inconsistency). This inconsistency was not anticipated in the protocol or statistical analysis plan and was resolved using medical judgement. The primary analysis was re-run with these patients considered PASI100 responders if PASI=0 and BSA=0 at Week 24.
aAssessed for patients with NAPSI >0 at baseline.
bAssessed for patients with LEI score >0 at baseline.
cAssessed for patients with SPARCC Enthesitis Index score >0 at baseline.
dAssessed for patients with LDI-B score >0 at baseline.
eAssessed for patients with HAQ-DI score ≥0.35 at baseline. A response of ≥0.35 CFB is the minimal clinically important difference in HAQ-DI.
Abbreviations: ACR, American College of Rheumatology; ADA, adalimumab; CFB, change from baseline; DAPSA, Disease Activity in Psoriatic Arthritis; HAQ-DI, Health Assessment Questionnaire-Disability Index; IXE, ixekizumab; LDA, Low Disease Activity; LDI-B, Leeds Dactylitis Index-Basic; LEI, Leeds Enthesitis Index; MDA, Minimal Disease Activity; PASI, Psoriasis Area and Severity Index; SPARCC, Spondyloarthritis Research Consortium of Canada; VLDA, Very Low Disease Activity